SRI AUROBINDO
ESSAYS IN PHILOSOPHY AND YOGA
SHORTER WORKS — 1910-1950
The Conservative Mind and Eastern Progress
The arrival of a new radical idea in the minds of men is the sign of a great coming change in human life and society; it may be combated, the reaction of the old idea may triumph for a time, but the struggle never leaves either the thoughts and sentiments or the habits and institutions of the society as they were when it commenced. Whether it knows it or not, it has gone forward and the change is irretrievable. Either new forms replace the old institutions or the old while preserving the aspect of continuity have profoundly changed within, or else these have secured for themselves a period of greater rigidity, increasing corruption, progressive deterioration of spirit and waning of real force which only assures them in the future a more complete catastrophe and absolute disappearance. The past can arrive at the most at a partial survival or an euthanasia, provided it knows how to compromise liberally with the future.
The conservative mind is unwilling to recognise this law though it is observable throughout human history and we can easily cull examples with full hands from all ages and all climes; and it is protected in its refusal to see by the comparative rarity of rapid revolutions and great cataclysmal changes; it is blinded by the disguise which Nature so often throws over her processes of mutation. If we look casually at European history in this light the attention is only seized by a few conspicuous landmarks, the evolution and end of Athenian democracy, the transition from the Roman republic to the empire, the emergence of feudal Europe out of the ruins of Rome, the Christianisation of Europe, the Reformation and Renascence together preparing a new society, the French Revolution, the present rapid movement towards a socialistic State and the replacing of competition by organised cooperation. Because our view of European history is chiefly political, we do not see the constant mutation of society and of thought in the same relief; but we can recognise two great cycles of change, one of the ancient races leading from the primitive ages to the cultured society of the Graeco-Roman world, the other from the semi-barbarism of feudal Christendom to the intellectual, materialistic and civilised society of modern times.
In the East, on the contrary, the great revolutions have been spiritual and cultural; the political and social changes, although they have been real and striking, if less profound than in Europe, fall into the shade and are apt to be overlooked; besides, this unobtrusiveness is increased by their want of relief, the slow subtlety of their process and the instinctive persistence and reverence with which old names and formulas have been preserved while the thing itself was profoundly modified until its original sense remained only as a pious fiction. Thus Japan kept its sacrosanct Mikado as a cover for the change to an aristocratic and feudal government and has again brought him forward in modern times to cover and facilitate without too serious a shock the transition from a mediaeval form of society into the full flood of modernism. In India the continued fiction of the ancient fourfold order of society based on spiritual idealism, social type, ethical discipline and economic function is still used to cover and justify the quite different, complex and chaotic order of caste which, while it still preserves some confused fragments of the old motives, is really founded upon birth, privilege, local custom and religious formalism. The evolution from one type of society to another so opposed to it in its psychological motives and real institutions without any apparent change of formula is one of the most curious phenomena in the social history of mankind and still awaits intelligent study.
Our minds are apt to seize things in the rough and to appreciate only what stands out in bold external relief; we miss the law of Nature's subtleties and disguises. We can see and fathom to some extent the motives, necessities, process of great revolutions and marked changes and we can consider and put in their right place the brief reactions which only modified without actually 
 preventing the overt realisation of new ideas. We can see for instance that the Sullan restoration of Roman oligarchy, the Stuart restoration in England or the brief return of monarchy in France with the Bourbons were no real restorations, but a momentary damming of the tide attended with insufficient concessions and forced developments which determined, not a return to the past, but the form and pace of the inevitable revolution. It is more difficult but still possible to appreciate the working of an idea against all obstacles through many centuries; we can comprehend now, for instance, that we must seek the beginnings of the French Revolution, not in Rousseau or Mirabeau or the blundering of Louis XVI, but in movements which date back to the Capet and the Valois, while the precise fact which prepared its tremendous outbreak and victory and determined its form was the defeat of the Calvinistic reformation in France and the absolute triumph of the monarchical system over the nobility and the bourgeoisie in the reigns of Louis XIII and Louis XIV. That double victory determined the destruction of the monarchy in France, the downfall of the Church and, by the failure of the nobles to lead faithfully the liberal cause whether in religion or politics, the disappearance of aristocracy.
preventing the overt realisation of new ideas. We can see for instance that the Sullan restoration of Roman oligarchy, the Stuart restoration in England or the brief return of monarchy in France with the Bourbons were no real restorations, but a momentary damming of the tide attended with insufficient concessions and forced developments which determined, not a return to the past, but the form and pace of the inevitable revolution. It is more difficult but still possible to appreciate the working of an idea against all obstacles through many centuries; we can comprehend now, for instance, that we must seek the beginnings of the French Revolution, not in Rousseau or Mirabeau or the blundering of Louis XVI, but in movements which date back to the Capet and the Valois, while the precise fact which prepared its tremendous outbreak and victory and determined its form was the defeat of the Calvinistic reformation in France and the absolute triumph of the monarchical system over the nobility and the bourgeoisie in the reigns of Louis XIII and Louis XIV. That double victory determined the destruction of the monarchy in France, the downfall of the Church and, by the failure of the nobles to lead faithfully the liberal cause whether in religion or politics, the disappearance of aristocracy.
But Nature has still more subtle and disguised movements in her dealings with men by which she leads them to change without their knowing that they have changed. It is because she has employed chiefly this method in the vast masses of the East that the conservative habit of mind is so much stronger there than in the West. It is able to nourish the illusion that it has not changed, that it is immovably faithful to the ideas of remote forefathers, to their religion, their traditions, their institutions, their social ideals, that it has preserved either a divine or an animal immobility both in thought and in the routine of life and has been free from the human law of mutation by which man and his social organisations must either progress or degenerate but can in no case maintain themselves unchanged against the attack of Time. Buddhism has come and gone and the Hindu still professes to belong to the Vedic religion held and practised by his Aryan forefathers; he calls his creed the Aryandharma, 
 the eternal religion. It is only when we look close that we see the magnitude of the illusion. Buddha has gone out of India indeed, but Buddhism remains; it has stamped its giant impress on the spirit of the national religion, leaving the forms to be determined by the Tantricism with which itself had made alliance and some sort of fusion in its middle growth; what it destroyed no man has been able to restore, what it left no man has been able to destroy. As a matter of fact, the double cycle which India has described from the early Vedic times to India of Buddha and the philosophers and again from Buddha to the time of the European irruption was in its own way as vast in change religious, social, cultural, even political and administrative as the double cycle of Europe; but because it preserved old names for new things, old formulas for new methods and old coverings for new institutions and because the change was always marked in the internal but quiet and unobtrusive in the external, we have been able to create and preserve the fiction of the unchanging East. There has also been this result that while the European conservative has learned the law of change in human society, knows that he must move and quarrels with the progressist only over the right pace and the exact direction, the Eastern or rather the Indian conservative still imagines that stability may be the true law of mortal being, practises a sort of Yogic āsana on the flood of Time and because he does not move himself, thinks – for he keeps his eyes shut and is not in the habit of watching the banks – that he can prevent the stream also from moving on.
the eternal religion. It is only when we look close that we see the magnitude of the illusion. Buddha has gone out of India indeed, but Buddhism remains; it has stamped its giant impress on the spirit of the national religion, leaving the forms to be determined by the Tantricism with which itself had made alliance and some sort of fusion in its middle growth; what it destroyed no man has been able to restore, what it left no man has been able to destroy. As a matter of fact, the double cycle which India has described from the early Vedic times to India of Buddha and the philosophers and again from Buddha to the time of the European irruption was in its own way as vast in change religious, social, cultural, even political and administrative as the double cycle of Europe; but because it preserved old names for new things, old formulas for new methods and old coverings for new institutions and because the change was always marked in the internal but quiet and unobtrusive in the external, we have been able to create and preserve the fiction of the unchanging East. There has also been this result that while the European conservative has learned the law of change in human society, knows that he must move and quarrels with the progressist only over the right pace and the exact direction, the Eastern or rather the Indian conservative still imagines that stability may be the true law of mortal being, practises a sort of Yogic āsana on the flood of Time and because he does not move himself, thinks – for he keeps his eyes shut and is not in the habit of watching the banks – that he can prevent the stream also from moving on.
This conservative principle has its advantages even as rapid progress has its vices and its perils. It helps towards the preservation of a fundamental continuity which makes for the longevity of civilisations and the persistence of what was valuable in humanity's past. So, in India, if religion has changed immensely its form and temperament, the religious spirit has been really eternal, the principle of spiritual discipline is the same as in the earliest times, the fundamental spiritual truths have been preserved and even enriched in their contents and the very forms can all be traced back through their mutations to the seed of the Veda. On the other hand this habit of mind leads to the 
 accumulation of a great mass of accretions which were once valuable but have lost their virtue and to the heaping up of dead forms and shibboleths which no longer correspond to any vital truth nor have any understood and helpful significance. All this putrid waste of the past is held to be too sacred to be touched by any profane hand and yet it chokes up the streams of the national life or corrupts its waters. And if no successful process of purification takes place, a state of general ill-health in the social body supervenes in which the principle of conservation becomes the cause of dissolution.
accumulation of a great mass of accretions which were once valuable but have lost their virtue and to the heaping up of dead forms and shibboleths which no longer correspond to any vital truth nor have any understood and helpful significance. All this putrid waste of the past is held to be too sacred to be touched by any profane hand and yet it chokes up the streams of the national life or corrupts its waters. And if no successful process of purification takes place, a state of general ill-health in the social body supervenes in which the principle of conservation becomes the cause of dissolution.
The present era of the world is a stage of immense transformations. Not one but many radical ideas are at work in the mind of humanity and agitate its life with a vehement seeking and effort at change; and although the centre of the agitation is in progressive Europe, yet the East is being rapidly drawn into this churning of the sea of thought and this breaking up of old ideas and old institutions. No nation or community can any longer remain psychologically cloistered and apart in the unity of the modern world. It may even be said that the future of humanity depends most upon the answer that will be given to the modern riddle of the Sphinx by the East and especially by India, the hoary guardian of the Asiatic idea and its profound spiritual secrets. For the most vital issue of the age is whether the future progress of humanity is to be governed by the modern economic and materialistic mind of the West or by a nobler pragmatism guided, uplifted and enlightened by spiritual culture and knowledge. The West never really succeeded in spiritualising itself and latterly it has been habituated almost exclusively to an action in the external governed by political and economic ideals and necessities; in spite of the reawakening of the religious mind and the growth of a widespread but not yet profound or luminous spiritual and psychical curiosity and seeking, it has to act solely in the things of this world and to solve its problems by mechanical methods and as the thinking political and economic animal, simply because it knows no other standpoint and is accustomed to no other method. On the other hand the East, though it has allowed its spirituality 
 to slumber too much in dead forms, has always been open to profound awakenings and preserves its spiritual capacity intact, even when it is actually inert and uncreative. Therefore the hope of the world lies in the re-arousing in the East of the old spiritual practicality and large and profound vision and power of organisation under the insistent contact of the West and in the flooding out of the light of Asia on the Occident, no longer in forms that are now static, effete, unadaptive, but in new forms stirred, dynamic and effective.
to slumber too much in dead forms, has always been open to profound awakenings and preserves its spiritual capacity intact, even when it is actually inert and uncreative. Therefore the hope of the world lies in the re-arousing in the East of the old spiritual practicality and large and profound vision and power of organisation under the insistent contact of the West and in the flooding out of the light of Asia on the Occident, no longer in forms that are now static, effete, unadaptive, but in new forms stirred, dynamic and effective.
India, the heart of the Orient, has to change as the whole West and the whole East are changing, and it cannot avoid changing in the sense of the problems forced upon it by Europe. The new Orient must necessarily be the result either of some balance and fusion or of some ardent struggle between progressive and conservative ideals and tendencies. If therefore the conservative mind in this country opens itself sufficiently to the necessity of transformation, the resulting culture born of a resurgent India may well bring about a profound modification in the future civilisation of the world. But if it remains shut up in dead fictions, or tries to meet the new needs with the mind of the schoolman and the sophist dealing with words and ideas in the air rather than actual fact and truth and potentiality, or struggles merely to avoid all but a scanty minimum of change, then, since the new ideas cannot fail to realise themselves, the future India will be formed in the crude mould of the Westernised social and political reformer whose mind, barren of original thought and unenlightened by vital experience, can do nothing but reproduce the forms and ideas of Europe and will turn us all into halting apes of the West. Or else, and that perhaps is the best thing that can happen, a new spiritual awakening must arise from the depths of this vast life that shall this time more successfully include in its scope the great problems of earthly life as well as those of the soul and its transmundane destinies, an awakening that shall ally itself closely with the renascent spiritual seeking of the West and with its yearning for the perfection of the human race. This third and as yet unknown quantity is indeed the force needed throughout the East. For at present we have only two 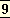
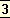
 extremes of a conservative immobility and incompetence imprisoned in the shell of past conventions and a progressive force hardly less blind and ineffectual because secondhand and merely imitative of nineteenth-century Europe, with a vague floating mass of uncertainty between. The result is a continual fiasco and inability to evolve anything large, powerful, sure and vital, a drifting in the stream of circumstance, a constant grasping at details and unessentials and failure to reach the heart of the great problems of life which the age is bringing to our doors. Something is needed which tries to be born; but as yet, in the phrase of the Veda, the Mother holds herself compressed in smallness, keeps the Birth concealed within her being and will not give it forth to the Father. When she becomes great in impulse and conception, then we shall see it born.
extremes of a conservative immobility and incompetence imprisoned in the shell of past conventions and a progressive force hardly less blind and ineffectual because secondhand and merely imitative of nineteenth-century Europe, with a vague floating mass of uncertainty between. The result is a continual fiasco and inability to evolve anything large, powerful, sure and vital, a drifting in the stream of circumstance, a constant grasping at details and unessentials and failure to reach the heart of the great problems of life which the age is bringing to our doors. Something is needed which tries to be born; but as yet, in the phrase of the Veda, the Mother holds herself compressed in smallness, keeps the Birth concealed within her being and will not give it forth to the Father. When she becomes great in impulse and conception, then we shall see it born.
Arya. 07.1916
{DocumentDescription}
{EndingDate}
{Year}
1916
{/Year}
{Month}
07
{/Month}
{Exactness}
Exact
{/Exactness}
{/EndingDate}
{DateType}
Publication
{/DateType}
{Source}
{SourceTitle}
Arya
{SourceType}
A Philosophical Review. Monthly
{/Source}
{WorkKind}
Essay
{/WorkKind}
{/DocumentDescription}
 preventing the overt realisation of new ideas. We can see for instance that the Sullan restoration of Roman oligarchy, the Stuart restoration in England or the brief return of monarchy in France with the Bourbons were no real restorations, but a momentary damming of the tide attended with insufficient concessions and forced developments which determined, not a return to the past, but the form and pace of the inevitable revolution. It is more difficult but still possible to appreciate the working of an idea against all obstacles through many centuries; we can comprehend now, for instance, that we must seek the beginnings of the French Revolution, not in Rousseau or Mirabeau or the blundering of Louis XVI, but in movements which date back to the Capet and the Valois, while the precise fact which prepared its tremendous outbreak and victory and determined its form was the defeat of the Calvinistic reformation in France and the absolute triumph of the monarchical system over the nobility and the bourgeoisie in the reigns of Louis XIII and Louis XIV. That double victory determined the destruction of the monarchy in France, the downfall of the Church and, by the failure of the nobles to lead faithfully the liberal cause whether in religion or politics, the disappearance of aristocracy.
preventing the overt realisation of new ideas. We can see for instance that the Sullan restoration of Roman oligarchy, the Stuart restoration in England or the brief return of monarchy in France with the Bourbons were no real restorations, but a momentary damming of the tide attended with insufficient concessions and forced developments which determined, not a return to the past, but the form and pace of the inevitable revolution. It is more difficult but still possible to appreciate the working of an idea against all obstacles through many centuries; we can comprehend now, for instance, that we must seek the beginnings of the French Revolution, not in Rousseau or Mirabeau or the blundering of Louis XVI, but in movements which date back to the Capet and the Valois, while the precise fact which prepared its tremendous outbreak and victory and determined its form was the defeat of the Calvinistic reformation in France and the absolute triumph of the monarchical system over the nobility and the bourgeoisie in the reigns of Louis XIII and Louis XIV. That double victory determined the destruction of the monarchy in France, the downfall of the Church and, by the failure of the nobles to lead faithfully the liberal cause whether in religion or politics, the disappearance of aristocracy.